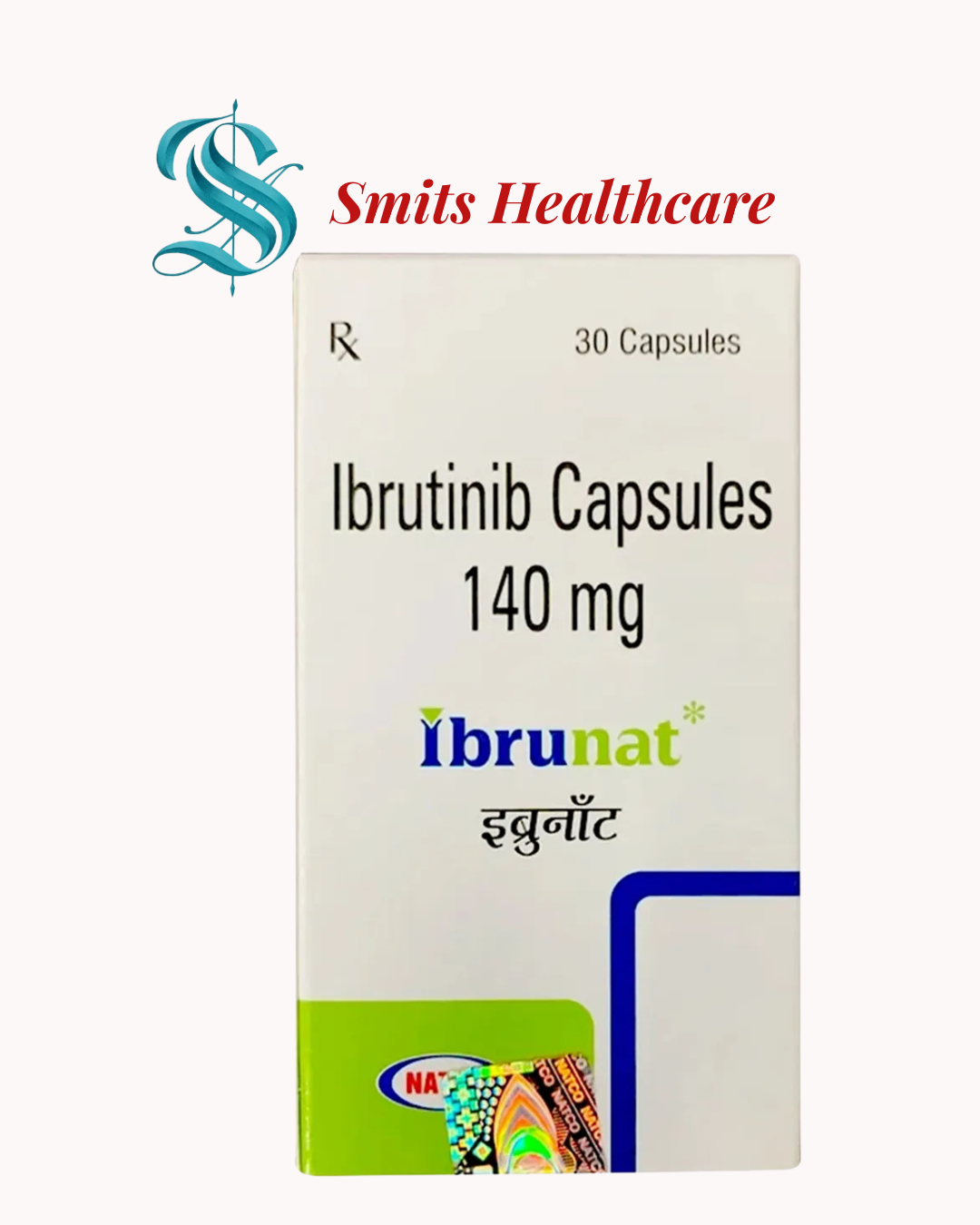
Ibrunat contains Ibrutinib, which is an oral targeted therapy used in the treatment of certain blood cancers. It is classified as a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. Ibrunat helps slow down or stop the growth of cancerous B-cells and is mainly prescribed for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, and some other B-cell malignancies.
Mechanism of action:
Ibrutinib works by irreversibly binding to the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) enzyme. This enzyme is an essential component of the B-cell receptor signaling pathway, which helps abnormal B-cells survive and multiply. By blocking BTK, Ibrunat interrupts these signals, leading to the death of cancerous B-cells and slowing disease progression.
Uses:
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)
-
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in patients who have received at least one prior therapy
-
Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM)
-
Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) in some cases
-
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) after failure of systemic therapy
Adverse effects:
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, tiredness, cough, muscle or joint pain, rash, and low blood counts. Serious adverse effects may include bleeding problems, atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat), infections, high blood pressure, and liver function changes. Long-term use can also increase the risk of secondary cancers