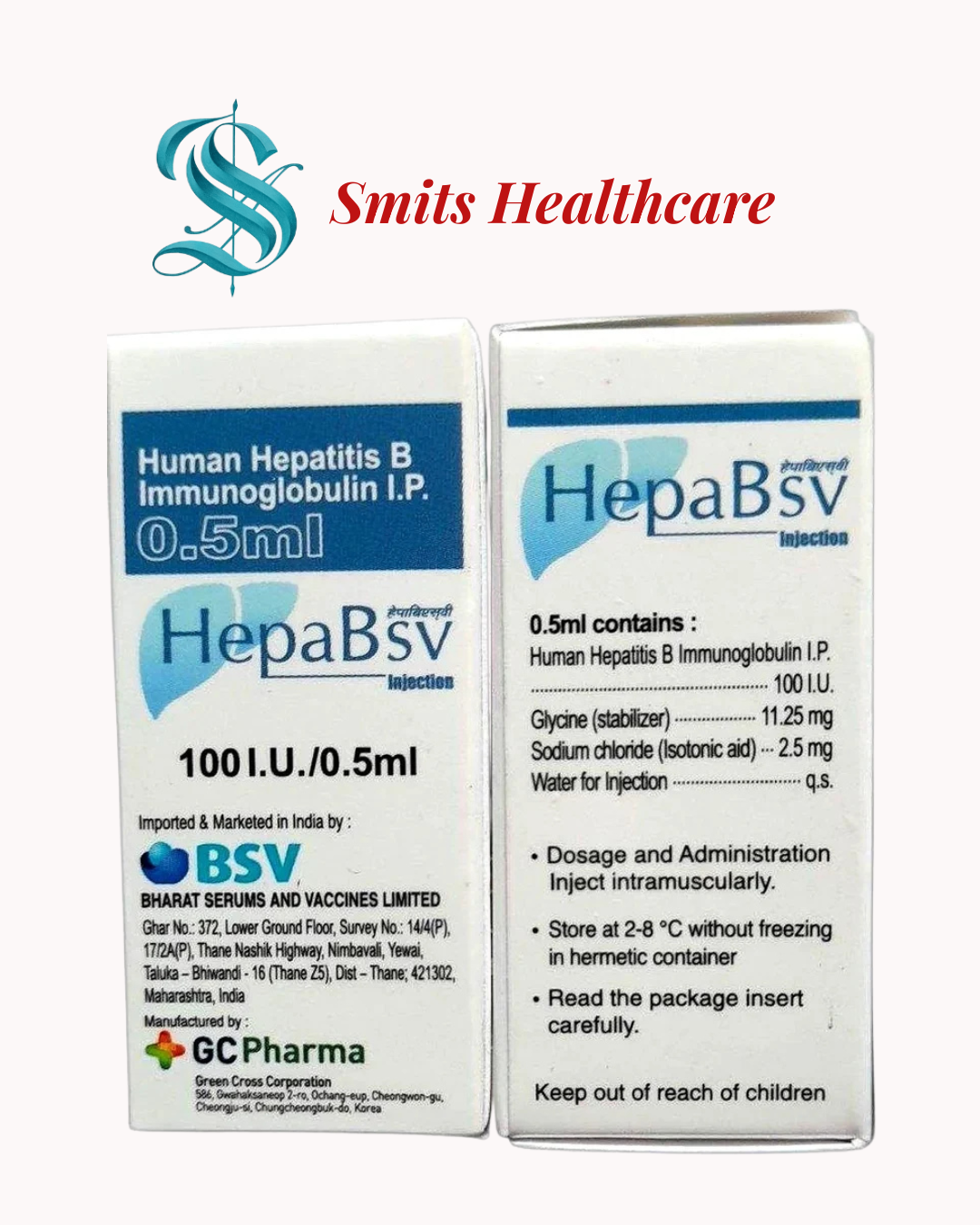
HepaBSV in this context refers to Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG), a preparation of antibodies against the hepatitis B virus (HBV). It is used to provide passive immunity — that is, immediate protection — against hepatitis B infection. HBIG is commonly given to people who have been exposed to hepatitis B virus, such as newborns of infected mothers, individuals after a needlestick injury, or patients undergoing liver transplant.
Mechanism of action:
Hepatitis B immunoglobulin contains preformed antibodies (anti-HBs) that bind to the hepatitis B virus. This neutralizes the virus and prevents it from infecting liver cells. Because it provides ready-made antibodies, HBIG offers immediate, short-term protection, unlike vaccines, which take time to generate the body’s own immunity.
Uses:
-
Post-exposure prophylaxis: after accidental exposure to hepatitis B (e.g., needle-stick injury)
-
Newborns of HBV-positive mothers: given at birth to prevent infection
-
Liver transplant patients: to prevent reinfection of the new liver by hepatitis B
-
Sometimes given alongside hepatitis B vaccination for better protection
Adverse effects:
Most patients tolerate HBIG well. Possible side effects include:
-
Mild pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site
-
Headache, fever, dizziness, or fatigue
-
Rare allergic reactions, including rash, itching, or difficulty breathing