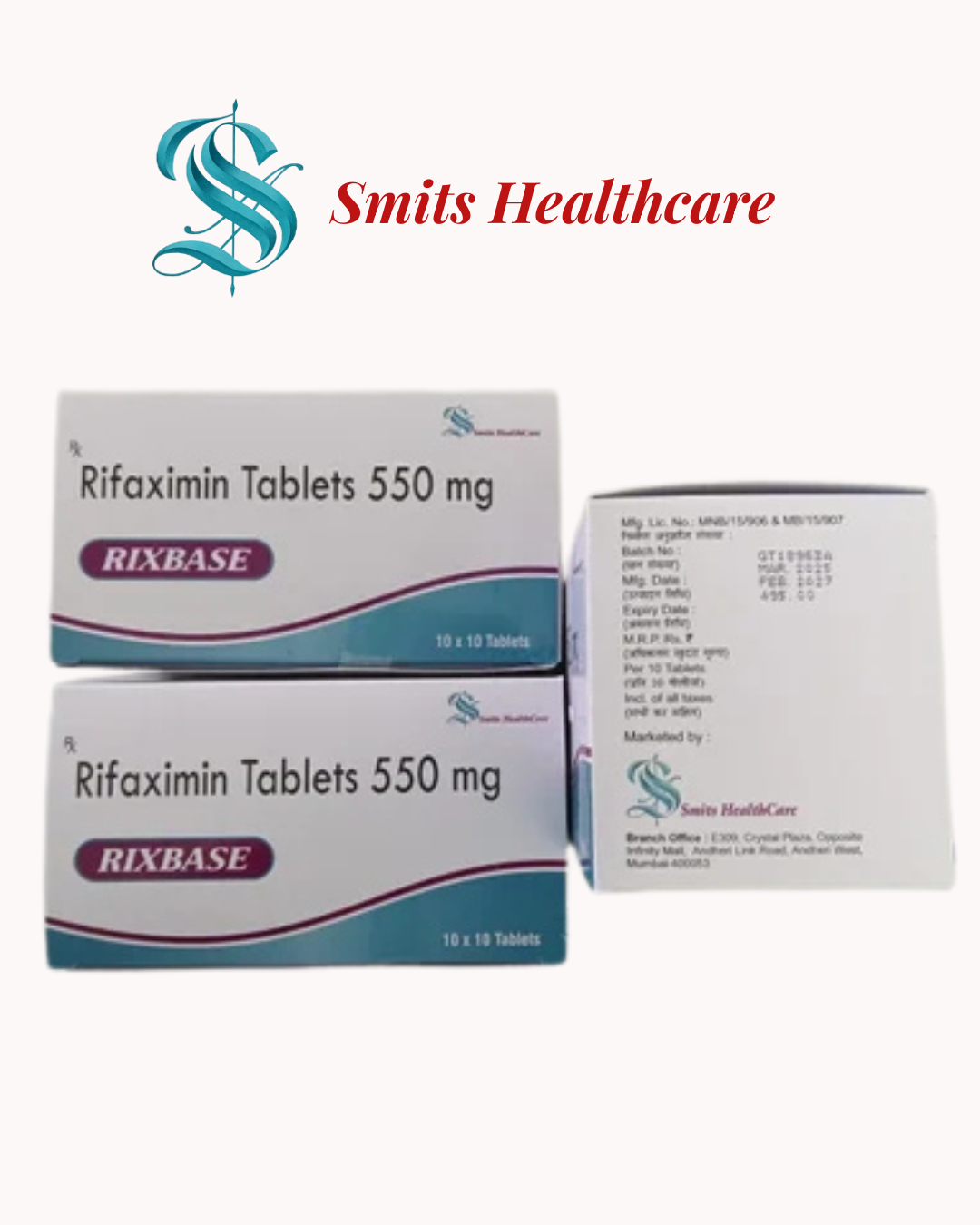
Rixbase contains rifaximin, a non-absorbable antibiotic that works locally in the intestines. Because it is not significantly absorbed into the bloodstream, it mainly acts inside the gut and has fewer systemic side effects compared to other antibiotics.
Mechanism of Action
-
Rifaximin binds to the beta-subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase, blocking the synthesis of bacterial RNA.
-
This stops the growth of bacteria in the intestines.
-
Since it is poorly absorbed, it stays in the gastrointestinal tract and is effective against gut-related infections and conditions.
Uses
Rixbase is used in adults for:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy: To reduce the risk of recurrence by lowering ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut.
-
Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D): To relieve abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
-
Traveler’s diarrhea (caused by certain bacteria, not by viruses or parasites).
Adverse Effects
Most patients tolerate it well. Possible side effects include:
-
Nausea
-
Flatulence (gas), abdominal pain
-
Headache
-
Constipation or diarrhea
-
-